








WHO Hospital Care for Children

Description of WHO Hospital Care for Children
The WHO e-Pocketbook of Hospital Care for Children is a mobile application developed to provide healthcare professionals with essential guidelines for managing children's health in hospital settings. This application serves as an electronic version of the Pocket Book of Hospital Care for Children and is designed for use on the Android platform, making it accessible for users who wish to download the app for offline access.
This app, created in collaboration with the World Health Organisation, The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne, the University of Melbourne, and Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, offers up-to-date, evidence-based clinical guidelines that are essential for medical practitioners, including doctors, nurses, and other health workers involved in the care of children. The guidelines focus specifically on major causes of childhood mortality prevalent in developing countries, addressing critical health issues that affect this vulnerable population.
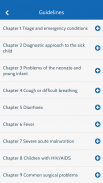
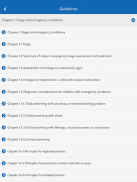
Users can navigate through various stages of management for every child, covering key areas such as Triage and Emergency treatment, History and Examination, Laboratory investigations, Supportive care and Monitoring, Discharge planning, and Follow-up. Each section is organized to facilitate quick reference and easy understanding, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions during patient care.
The app prioritizes major neonatal illnesses, such as low birth weight, prematurity, sepsis, perinatal asphyxia, and congenital anomalies. The guidelines are structured to aid in the effective treatment of these conditions, ensuring that healthcare workers have access to the latest information and recommendations to improve patient outcomes.
Pneumonia and other respiratory issues, including bronchiolitis, asthma, and tuberculosis, are also covered in detail. The app outlines management strategies for these conditions, providing healthcare professionals with the tools necessary to address common respiratory illnesses that affect children globally.
In addition, the WHO e-Pocketbook includes guidance on managing diarrheal diseases, both acute and chronic. This feature is particularly important, as diarrhea remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in children, especially in low-resource settings. The app provides evidence-based approaches to treatment and prevention, equipping healthcare workers with vital knowledge to combat this health challenge.
Fever management, including illnesses such as malaria, meningitis, septicemia, and rheumatic fever, is another critical area addressed within the app. The guidelines offer specific protocols for diagnosing and treating these conditions, which are prevalent in many regions, particularly in developing countries.
Severe acute malnutrition is also a focus of the app, with detailed management guidelines designed to assist healthcare providers in identifying and treating affected children. This aspect of the app is crucial for improving nutritional outcomes and overall health in vulnerable populations.
HIV/AIDS management is included, providing healthcare workers with essential information on the care and treatment of children living with this condition. The app emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and continuous monitoring, helping to ensure that children receive appropriate care.
Surgical problems, including trauma and burns, are addressed as well. The app offers guidance on the initial assessment and management of these urgent conditions, ensuring that healthcare workers are prepared to handle surgical emergencies effectively.
With the ability to view all guidelines offline and the promise of regular updates, the app remains a reliable resource for healthcare professionals. The combination of comprehensive guidelines and the ability to access information without the need for an internet connection enhances the usability and practicality of the application in various clinical settings.
The WHO e-Pocketbook of Hospital Care for Children stands out as a vital tool for healthcare providers who care for children in hospitals. By focusing on major health challenges faced by children in developing countries, the app equips professionals with the necessary knowledge and resources to improve health outcomes and provide effective care.
In summary, this application is a valuable resource for those involved in pediatric care, emphasizing evidence-based practices and up-to-date guidelines across various health concerns. The app’s design caters to the needs of healthcare professionals, ensuring that they have ready access to critical information while working to enhance the health and well-being of children.
For further information, visit the relevant organizations involved in the development of the app.

























